Mid Term Project Update
Abstract:
Tactics and strategies for sports are largely depicted on the top-view of game field. For a lot of sport analytics to happen, we need to convert the camera view broadcast stream to a top view that helps understand player movements in-game. This is typically achieved with an expensive multi-camera set up around the field. In this work, we aim to solve this problem with computer vision techniques. We implement a method to do this in a semi supervised way. We generate homographies between images from particular camera views to the corresponding location in the top view field (which is an edge map) and create a large database of such edge maps along with homography matrices using camera perturbations. During test time, we can use a pix2pix deep network trained on our database obtained in this way to obtain corresponding edge map. This is queried through the database to get a homography matrix which obtains a top view of that test image. In this way, we can obtain relevant statistics from just the broadcast video stream of the match via an efficient solution that does not require any expensive camera setup.
Approach and Experiments:
- Obtaining a top view projection of the training image: We use the FIFA 2014 World Cup Dataset for football images and create the homographies to map image from camera view to top view.
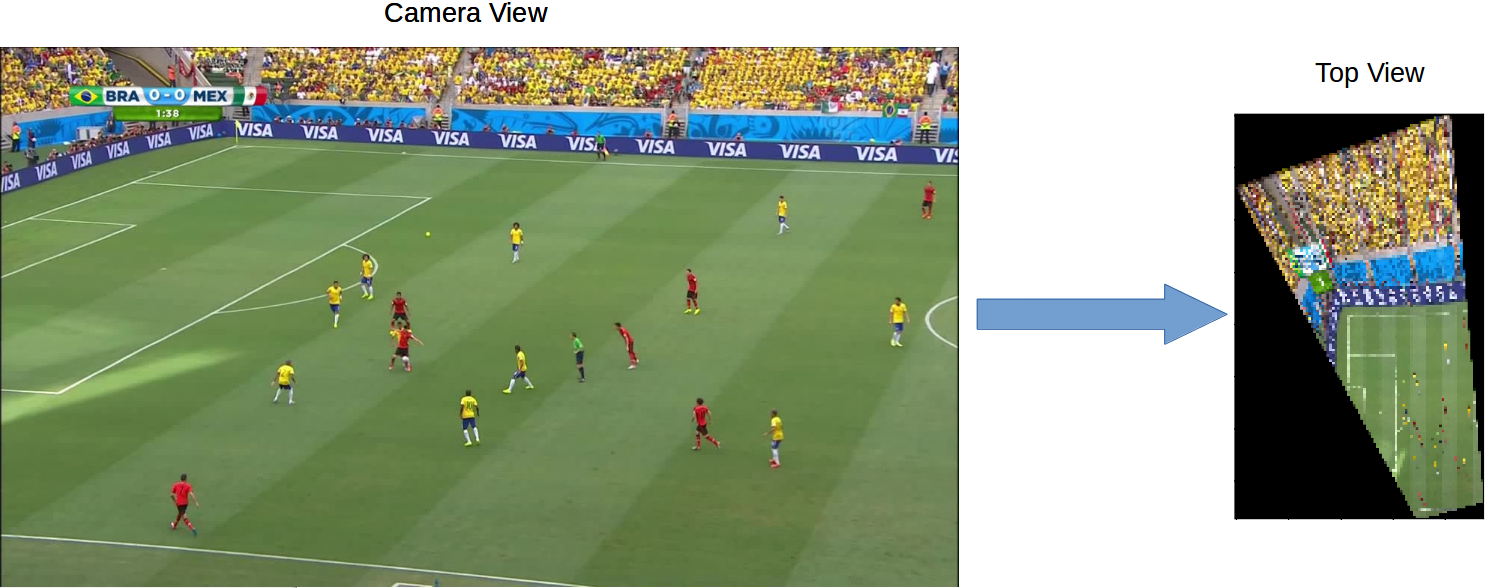 a) Camera View to Top View
a) Camera View to Top View
- Perturbations: We map each camera-view image to the top-view and find the corresponding top-view edge map of the football field.
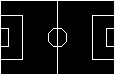 b) Football Field top-view edge map
b) Football Field top-view edge map
To each edge map in the top view, we apply perturbations of the type- pan, zoom and tilt. We create new homographies to map these perturbed trapeziums in top-view to rectangular images (of the original size). Using these edge-maps in the camera view and the associated inverse homography, we build a dictionary that maps an edge map in the camera-view to the corresponding homography that transforms it to the top-view.
Perturbation equations:
Pan: We simulate pan by rotating the quadrilateral (q0, q1, q2, q3) around the point of convergence of lines q0q3 and q1q2 to obtain the modified quadrilateral.
Zoom: We simulate zoom by applying a scaling matrix to the homogenous coordinates of q0, q1, q2 and q3.
Tilt: We simulate tilt by moving the points q0, q1, q2 and q3 up/ down by a constant distance along their respective lines q0q3 and q1q2.
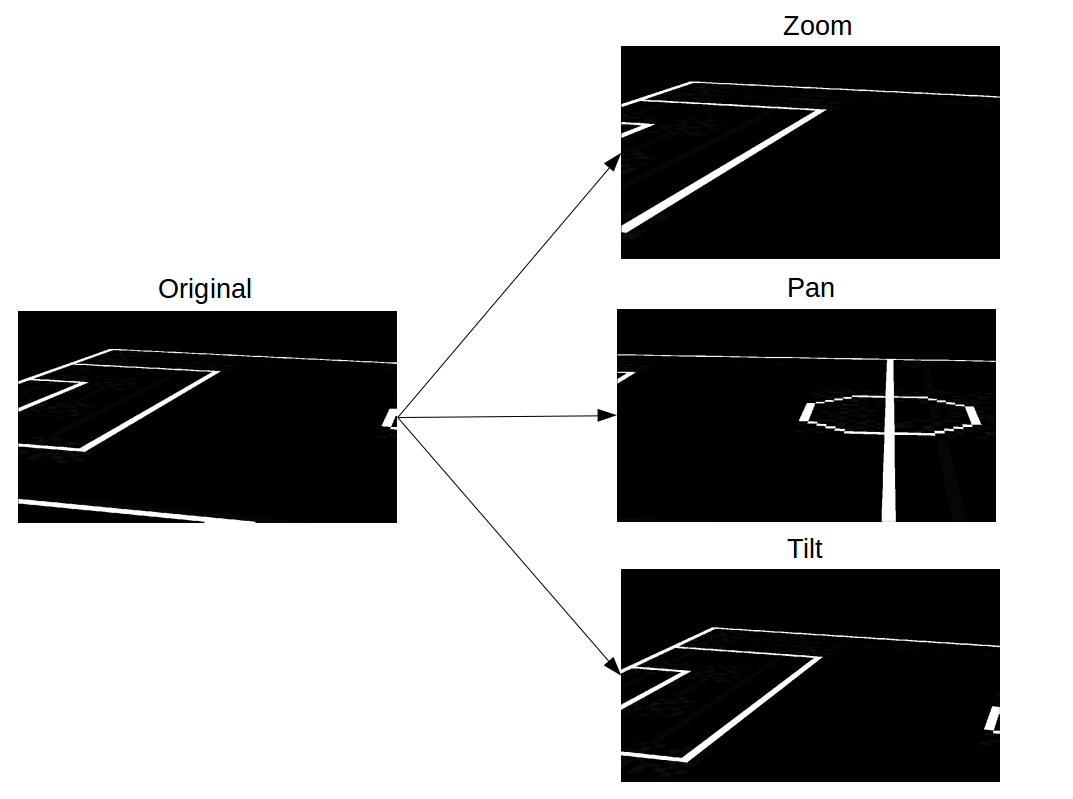 c) Perturbations- Pan, Tilt and Zoom
c) Perturbations- Pan, Tilt and Zoom
- Generating edge maps: We use pix2pix to generate edge maps from camera images. We compile the set of images from the camera view as source images- S. We generate the edge map for these images by using the inverse homography found in step 1 applied to the top-view football field edge map. We call these target images- T. We train pix2pix to learn a mapping from S -> T. For test images, we convert the image from camera view to an edge map using our trained pix2pix model. Further, we find the closest edge map in our dictionary to lookup the homography we can use to transform the input image to top-view.
Pix2Pix is a conditional GAN which takes an input image x and translates it to a target domain y. Adversarial supervision exists to make generated outputs i.e G(x) look similar to the data distribution of y. There is also supervision based on the ground truth data in terms of L1 loss.
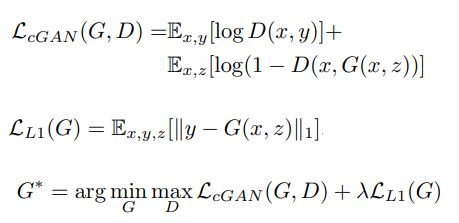 d) GAN equations
d) GAN equations
During test time, the query image is passed through the generator to obtain the corresponding edge map which can be used for matching with the database.
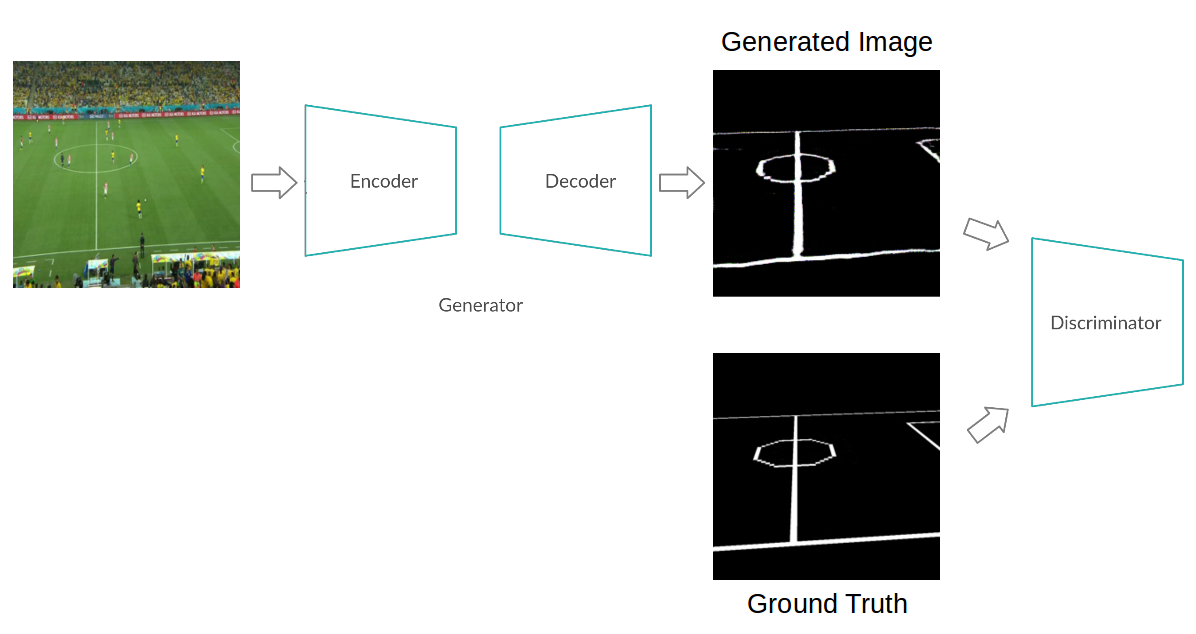 e) Adversarial training pipeline for edge map generation using Pix2Pix
e) Adversarial training pipeline for edge map generation using Pix2Pix
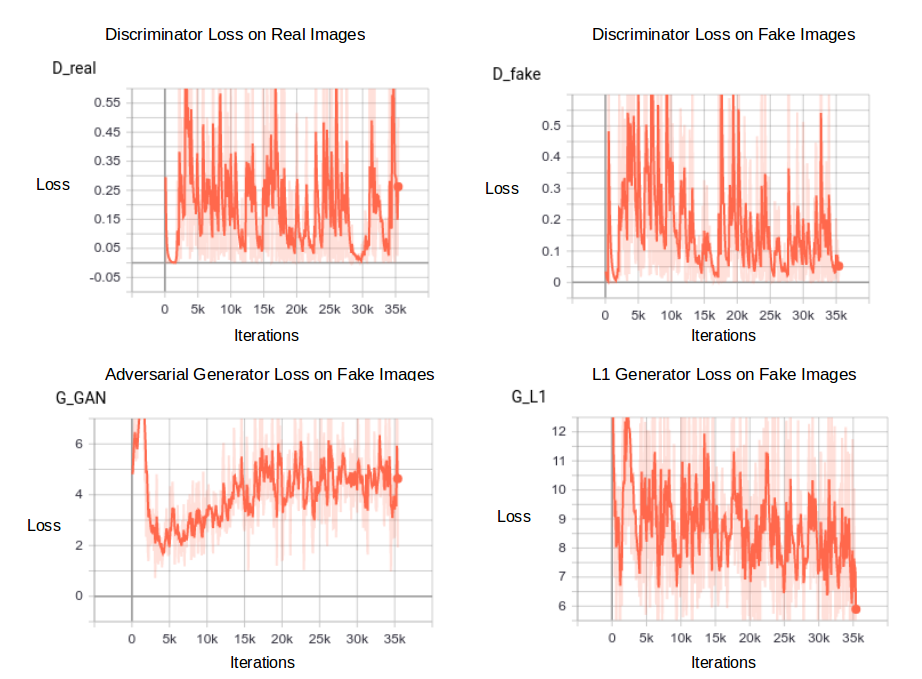 f) Pix2Pix Training Loss Curves
f) Pix2Pix Training Loss Curves
Up next:
-
Obtaining top view projecting during testing: Use a KNN approach to find the closest match in the dictionary to the edgemap from the input image. The best match would be obtained based on which samples give minimum distance in terms of chamfer distance, HOG features, SIFT features, etc.
-
Player Detection: Use an unsupervised clustering approach like DBScan or superpixel based segmentation to obtain the approximate location of a player and map it to top-view.
-
Measuring Accuracy: Since there is no absolute metric and we don’t have ground truth for test images (of player positions in top-view), we plan to qualitatively assess the correctness of the top-view images generated. We just plan to use something like a MOS score to evaluate the accuracy of our final model on test images. Also, we do have the homographies for transforming the camera-view images to top-view (for the test segment of our dataset) and we plan to use a measure like RMSE to quantify the error in finding the closest match for homography from the dictionary we construct.